Your Guide to Early Detection
Quick downloadable tips for early detection (download the guide)
Know your skin: It is important to note any changes to your skin. Use the following as a general guide when performing monthly self-skin exams.
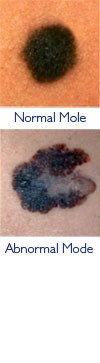
A: Asymmetry. If you were to divide the mole in half vertically, would it be the same on both sides? What if you divide it in half horizontally, or diagonally? You want your moles to be the same no matter which way you divide it in half.
B: Border. What does the border of your mole look like? Is it smooth? Is it irregular, blurred or poorly defined? The border of your moles should be smooth, well defined, and even.
C: Color. While benign moles are typically a single shade of brown, melanoma may have a variety of colors including shades of black, brown, or tan. Melanoma may also have shades of white, red, and even blue. You want to make sure your mole does not have different shades of the same color or completely different colors from one area to the next.
D: Diameter. How large is your mole? Melanoma can be in any sized mole, but most healthy moles do not exceed the size of a pencil eraser, which is about ¼ of an inch or six millimeters. If your mole is bigger it should be examined by a dermatologist.
E: Evolving. Has your mole been changing over time? The best tip here is to take a picture of it every month so you can compare each time you do a self-exam. You are looking for any difference here—color, shape, or size.
Using what is termed the "ugly duckling" description is also helpful. If you see a mole that does not look normal, or looks different than any other mole or lesion on the body, have it checked by a dermatologist or other trained medical professional.
Also see a dermatologist if you find a mole that does not pass one or more of the ABCDEs of melanoma or have a mole that itches or bleeds or if you find a nodule under your skin. It is better to get checked by a medical professional just to be safe.
MORE ABOUT MELANOMA
CLINICAL TRIALS FOR MELANOMA
OTHER SKIN CANCERS
SKIN CANCER IN PEOPLE OF COLOR
TIPS FOR PREVENTION
A PATIENT'S GUIDE TO IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY